Educational
9
min read
Micro-Credentials: Everything You Need to Know
Micro-credentials are revolutionizing education and professional development, offering learners a pathway to acquire and validate specific skills efficiently. As the job market demands specialized skills, micro-credentials have emerged as a valuable tool for individuals seeking to advance their careers and for organizations aiming to upskill their workforce. These digital credentials represent a focused, competency-based approach to learning, providing targeted learning opportunities and enabling individuals to showcase their expertise in a particular area. Higher education institutions and other organizations now offer micro-credentials to meet this growing demand.
What are Micro-Credentials?
Micro-credentials are targeted certifications that validate the acquisition of specific knowledge and skills. Unlike a full degree, a micro-credential focuses on a particular competency, such as proficiency in a software program or mastery of a specific skill. These credentials offer learners a way to demonstrate expertise and signal to employers that they possess in-demand abilities. The rise of online learning has further fuelled the popularity of micro-credentials, making education and training more accessible and flexible for learners worldwide.
Types of Micro-Credentials
Micro-credentials come in various forms, each designed to validate different competencies. Some micro-credentials focus on technical skills, such as data analytics or cybersecurity, while others emphasize soft skills, like leadership or communication. Many higher education institutions now offer micro-credential programs as part of their continuing education credits, allowing learners to earn micro-credentials for completing specific coursework or projects. In particular, the following type is becoming increasingly popular in higher education:
Stackable credit bearing micro-credentials allow learners to accumulate multiple credentials.
These credentials build upon each other to demonstrate expertise in a broader area.
The visual given below illustrates a credential ecology in higher education that maps different types of learning credentials across two dimensions: credit-bearing vs. non-credit-bearing (vertical axis) and bundled vs. unbundled learning (horizontal axis).
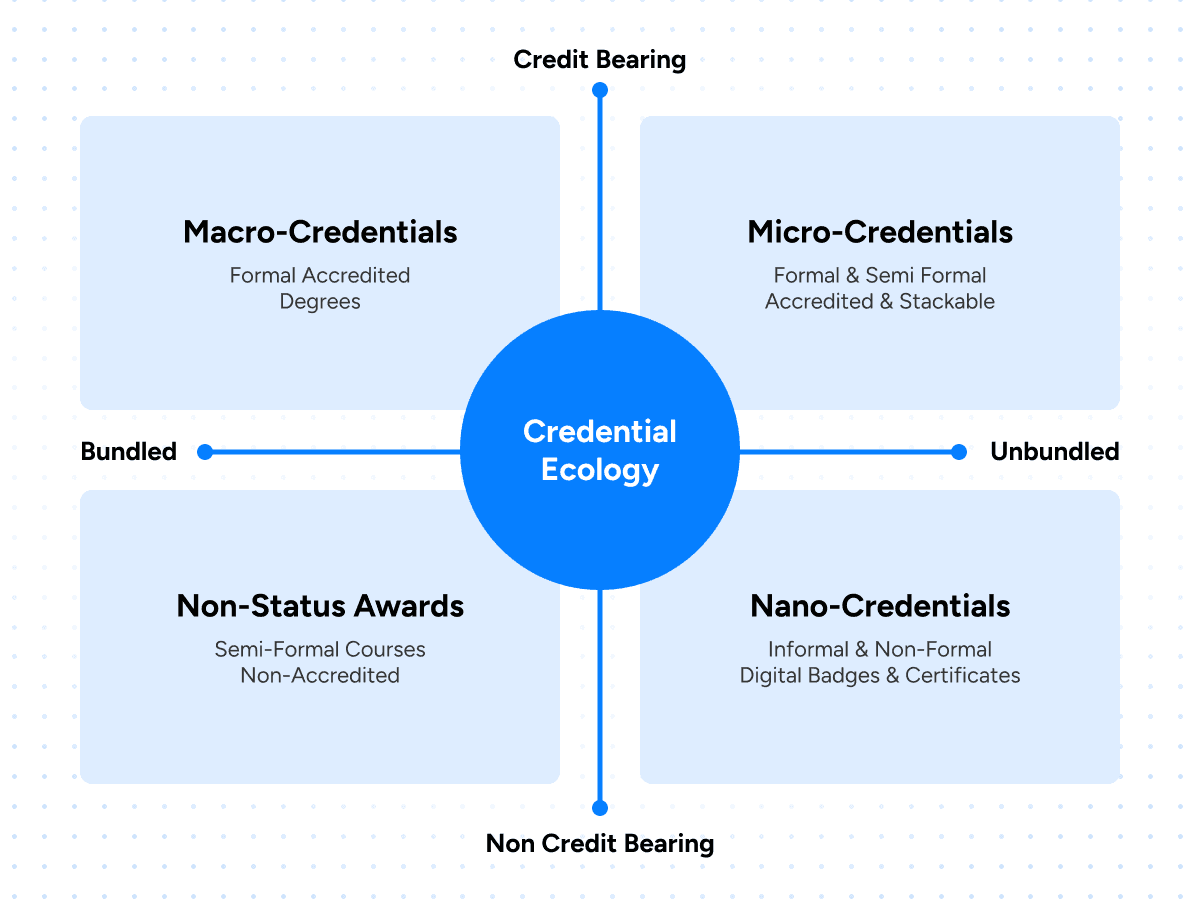
Macro-Credentials: These are fully bundled, credit-bearing qualifications that are formally accredited, such as university degrees or diplomas (Bachelor’s degree in Engineering or an MBA). They represent long-term, comprehensive programs with high institutional recognition.
Micro-Credentials: These are smaller, modular credentials that are often credit-bearing or formally recognized and can be stacked toward a larger qualification (university-issued certificate in Data Analytics or Cybersecurity that counts toward a degree).
Non-Status Awards: These are semi-formal learning recognitions that are not accredited and do not carry academic credit, such as professional development courses, bootcamps, or industry workshops that provide skills but limited formal recognition.
Nano-Credentials: These are highly granular, non-credit-bearing credentials that recognize specific skills or learning outcomes, such as digital badges or completion certificates for short courses, platform-based learning, or internal corporate training.
How Micro-Credentials Differ from Traditional Credentials
Unlike traditional credentials, such as a full degree, micro-credentials offer a more focused and flexible approach to learning. Micro-credentials validate specific skills and competencies, allowing learners to quickly acquire and demonstrate expertise in in-demand areas. Many learners showcase their digital credentials on their LinkedIn profile. These digital credentials provide immediate value in the job market. The competency-based nature of micro-credentials ensures that learners acquire practical, job-relevant skills, making them highly attractive to employers seeking specialized talent.

Subject | Traditional Credentials | Micro-Credentials |
|---|---|---|
Scope | Broad, comprehensive programs | Focused, skill-specific learning |
Duration | Long-term (years) | Short-term (weeks or months) |
Structure | Bundled into a single qualification | Modular and stackable |
Flexibility | Limited customization | Highly flexible and learner-driven |
Example | B.Tech, MBA, PhD | 20 Hour Course - 8 modules |
Benefits of Micro-Credentials
Advantages for Learners
The benefits of micro-credentials for learners are vast and varied, especially in today's rapidly evolving job market. By focusing on specific skills and competencies, micro-credentials enable learners to quickly acquire new skills and validate their expertise in particular areas. This competency-based approach is particularly appealing to learners who want to advance their careers without committing to a full degree program. Offered online and often stackable, micro-credentials enhance access to education and training, providing learners with more flexible and tailored learning opportunities. Displaying a digital badge on a LinkedIn profile after completing a micro-credential program can significantly improve career prospects.
Benefits for Employers
Employers stand to gain significantly from the adoption of micro-credentials within their organizations. Micro-credentials validate that job candidates possess specific skills and competencies, reducing the need for extensive training. Higher education institutions and other organizations offer micro-credentials to meet the demand for specialized skills. By recognizing micro-credentials, employers can more effectively identify and recruit individuals with in-demand capabilities. Furthermore, offering micro-credentials as part of professional development initiatives can help upskill current employees, boosting overall productivity and reducing turnover rates. These digital credentials provide a clear signal of an individual's expertise and commitment to continuous learning.
Micro-Credentials and Lifelong Learning
Micro-credentials play a pivotal role in promoting lifelong learning, encouraging individuals to continually acquire knowledge and skills throughout their careers. The flexibility and accessibility of micro-credentials make it easier for learners to engage in ongoing professional development, earning micro-credentials in areas of interest or relevance. These digital credentials offer a way for individuals to demonstrate their commitment to staying current with industry trends and best practices, adding value to their LinkedIn profiles. Stackable micro-credentials facilitate a structured approach to lifelong learning, enabling individuals to build upon existing competencies and achieve mastery in a broader subject area. Learners can earn micro-credentials through coursework.
How Micro-Credentials Work
Structure of a Micro-Credential
The structure of a micro-credential is designed to ensure that learners acquire and demonstrate mastery of specific skills and knowledge. Typically, a micro-credential program includes several key components, such as:
A defined set of learning outcomes
Assessment criteria and required coursework
The competency-based nature of micro-credentials means that learners must demonstrate proficiency in each skill or area before earning the credential. Higher education institutions and other organizations carefully design these programs to align with industry standards and employer needs. A digital badge is often awarded upon successful completion, providing a visible representation of the learner's achievement.
Assessment and Evaluation
Assessment and evaluation are critical components of the micro-credentialing process, ensuring that learners have genuinely acquired the specific skills and knowledge being validated. A variety of methods are employed to assess learners, including:
Quizzes and exams to gauge theoretical understanding.
Projects and performance-based assessments to demonstrate practical application.
The goal is to evaluate the learner's ability to apply their knowledge in practical, real-world scenarios. A digital badge is only issued when the learner demonstrates a satisfactory level of competency. Credentialing organizations often use rubrics and other standardized assessment tools to ensure fairness and consistency in the evaluation process. By validating these competencies, micro-credentials enhance the credibility of the learner.

Digital Badges and Recognition
Digital badges serve as a visual representation of the micro-credential earned, providing learners with a tangible way to showcase their accomplishments. These badges are:
Sharable: Easily shared on social media platforms like LinkedIn, allowing learners to signal their expertise to potential employers and professional networks.
Stackable: They allow learners to progress step by step, validating specific skills while working toward larger academic or professional outcomes via learning pathways.
Informative: The metadata embedded within a digital badge provides detailed information about the skills, earning criteria, endorsements and competencies which adds credibility to the credential.
Verifiable: Recognition of micro-credentials by employers and industry organizations is essential for their widespread adoption and acceptance. Digital badges offer a convenient and effective way for learners to validate their achievements and advance their careers.
Portable: Open Badge compliant credentials ensure cross-platform compatibility and interoperability across systems and providers.
Available Micro-Credentials
Popular Fields Offering Micro-Credentials
Numerous fields now offer micro-credentials to meet the increasing demand for specialized skills. Popular areas include information technology, data analytics, marketing, and healthcare. Higher education institutions and industry organizations are increasingly developing micro-credential programs to address specific skill gaps within these sectors. Learners can earn micro-credentials in areas such as cybersecurity, project management, digital marketing, and data science. These micro-credentials validate the learner's proficiency in in-demand skills, enhancing their appeal to potential employers and their ability to advance their careers within these rapidly evolving industries. The availability of these digital credentials reflects the changing nature of the job market.
Stackable Micro-Credentials
Stackable micro-credentials represent a strategic approach to professional development, enabling learners to accumulate multiple credentials that build upon one another. These stackable micro-credentials allow individuals to develop expertise in a particular area, validating their knowledge and skills in a progressive manner. Many higher education institutions offer micro-credential programs designed to be stackable, allowing learners to earn micro-credentials over time and ultimately achieve a more comprehensive certification. Learners can often showcase their stackable digital credentials on their LinkedIn profile. The competency-based framework ensures the learners’ progressive mastery and signals their continued commitment to learning new skills. This approach also offers a pathway to a full degree or other traditional credential.
Designing a Micro-Credential
Designing an effective micro-credential requires clearly defined learning outcomes, measurable earning criteria, and robust assessment methods that align with real-world skill requirements. The credential should be mapped to industry-relevant competencies and structured to support stackability, enabling learners to build toward larger qualifications over time. Equally important is the digital representation of the credential, ensuring it is verifiable, shareable, and portable across platforms. Solutions such as Wauld support coaches, educators and training providers in designing, issuing, and managing micro-credentials that meet these standards while maintaining trust, transparency, and long-term value for learners.
Choosing the Right Micro-Credential for a Learner
Selecting the appropriate micro-credential requires careful consideration of career goals and the learner’s current skill set. It is important to identify the specific skills and competencies that are in demand within the relevant industry or the area the learner aspires to work in. Various micro-credential programs offered by higher education institutions or professional organizations should be researched, with close attention paid to the curriculum, assessment methods, and recognition by employers. Ensuring that the micro-credential aligns with professional development objectives helps strengthen its impact on career progression. Micro-credentials that address skill gaps can significantly enhance credibility in the job market, and earning a digital badge serves as a strong addition to a LinkedIn profile.
Advancing Career with Micro-Credentials
Micro-Credentials in Professional Development
Micro-credentials are a powerful tool for professional development, providing targeted learning opportunities to enhance specific skills and competencies. Individuals can earn micro-credentials to validate their expertise in in-demand areas, signaling their commitment to continuous learning. Higher education institutions and organizations often offer micro-credentials as part of their professional development programs, allowing employees to upskill and stay current with industry trends. The flexibility of micro-credentials makes them accessible to working professionals. Digital credentials can be shared on a LinkedIn profile. This approach enables individuals to advance their careers by offering education and training.
Case Studies of Career Advancement
Numerous case studies highlight the transformative impact of micro-credentials on career advancement. For instance, individuals who earn micro-credentials in data analytics have reported significant increases in job opportunities and salary. Professionals in marketing have leveraged micro-credentials to demonstrate their expertise in digital marketing strategies, leading to promotions and new career paths. These success stories underscore the value of micro-credentials in validating skills and competencies. Learners showcase their newly acquired skills by posting their digital badge to their LinkedIn profile. Employers appreciate the tangible evidence of skills. Micro-credentials are not a full degree but a specialized skill.

Future Trends in Micro-Credentials
The future of micro-credentials is poised for continued growth and innovation. As the job market demands increasingly specialized skills, the demand for micro-credentials will likely increase. Expect to see greater integration of micro-credentials into higher education curricula and professional development programs, with more higher education institutions offering micro-credentials. Online learning platforms will continue to expand their offerings, providing learners with a wider range of micro-credential opportunities. The recognition and acceptance of micro-credentials by employers will also grow, further solidifying their value in the job market. Validate your skills and post a digital badge on your LinkedIn profile.






